By performing diverse approach from in and out of AV fistula,
fast recovery, precise treatment, and minimal side effect are being accomplished.
- AV fistula treatment
- Hybrid treatment that incorporates intervention and surgical treatment
Treatment of AV fistula
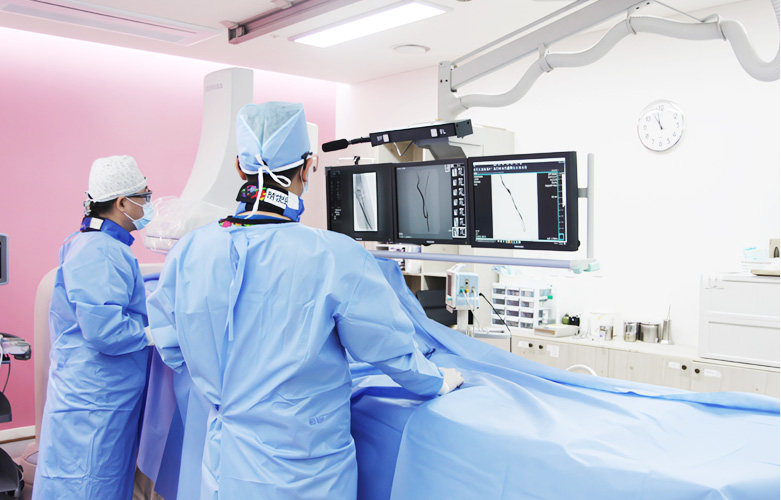
Blocking, swelling, and becoming numb everyday, AV fistula problem that repeats over and over. We will be your ‘trustworthy companion’ so that you won’t be alone in the endless fight that will follow you for lifetime. MINT hospital Vascular Center achieves fast recovery, precise treatment, and minimal side effect with diverse approach from in and out of AV fistula,.
-
AV fistula recanalization
procedure
- Stent insertion
- Balloon angioplasty
- Thrombectomy
-
HYBRID CARE
AV fistula
hybrid treatment
-
Dialysis access surgery
- AVF (Autologous AV fistula)
- AVG (Artificial dialysis graft)
Corrective surgery
- Av fistula reduction
- Vein superficialization
- Dialysis streamline surgery
- Pseudoaneurysm resection
- peripheral vessel ligation
Procedure
AV fistula Recanalization
Intervention (non-surgical)
that treats AV fistula complications.
-
-
What is
AV fistula recanalization ?
-
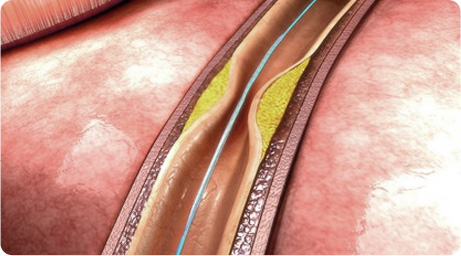
It can treat conditions like stenosis, occlusion, thrombosis, and calcification that induces circulatory disorder in AV fistula. It recanalizes narrowed or occluded fistula by inserting fine medical device (catheter) intravascularly. It is also called ‘Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)’ or ‘percutaneous recanalization’ It is performed by intervention radiologist.
-
-

Expansion and speed
-
State-of-the-art medical device is attached to the catheter depending on stenosis in the fistula to conduct more detailed
treatments like stent insertion, balloon angioplasty, and thrombectomy. Recanalization has its advantage in that it can immediately treat the problem in any segments, from AV fistula to vein entering the heart, and dialysis is available right after the procedure
-
 Local anesthesia +
minimal invasion Minimal
physical fatigue
Local anesthesia +
minimal invasion Minimal
physical fatigue
-
 After
After
recanalization
Immediate dialysis
-
 From test to
From test to
procedure
ONE STOP treatment
-
 Recurred
Recurred
at the same site
Revisional surgery
OK
-
 95% treatment
95% treatment
of AV fistula complication
High recanalization success rate
-
 Multiple
Multiple
stenosis
Treated
all at once
Procedure process
-
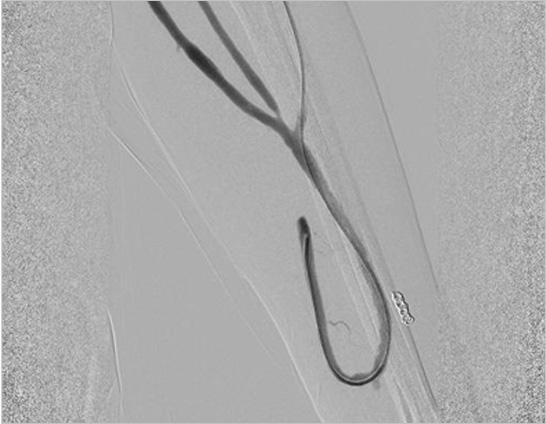
Insertion at the occlusion
-
Destruction of the occlusion
-
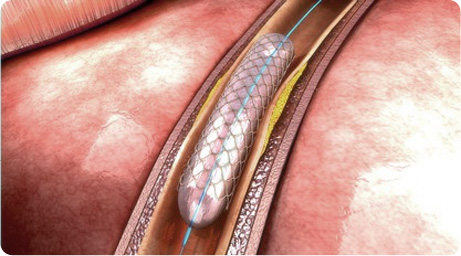
After inserting balloon catheter at the section of fistula occluded by thrombus, balloon is inflated to expand the causative fistula. As the occluded fistula is recanalized, the blood circulation returns to normal.
-
Local anesthesia ▶
Small incision of
1.5mm in the skin ▶
Guide wire insertion
-
Insertion of catheter
with balloon, drug,
or stent (metal net) based
on the purpose
of the treatment
-
Contrast injection
with catheter ▶
Angiographic X-ray
imaging in real time
-
Catheter approaches
the lesion via blood
vessels to treat stenosis,
occlusion, thrombosis,
and calcification
-
Removal of
surgical device ▶
Immediate dialysis
Treatment outcome
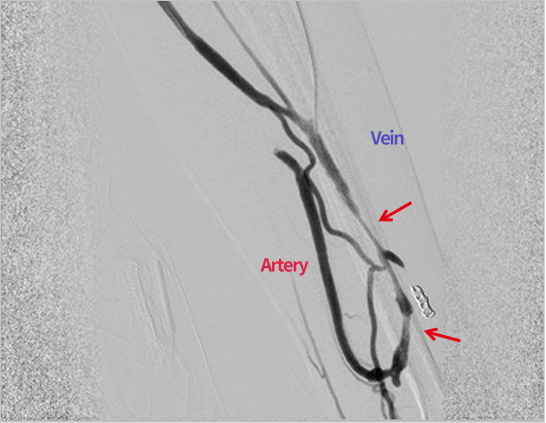
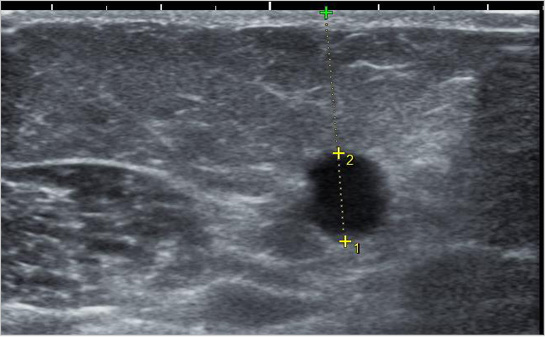
AV fistula is underdeveloped due to stenosis before the treatment (shown in arrow), making only artery visible and leaving the vein occluded.
After treatment, the blood flow returns to normal and vein is visible
surgery
Dialysis access surgery
Surgery to create a new AV fistula
by connecting artery and vein
What is dialysis access surgery?
It connects artery and vein directly or via artificial graft, creating a new dialysis channel (access).
After the surgery, AV fistula that has matured for 1~3 months can be used without problem only after satisfying the following conditions
- ① Adequate blood flow (500mL per minute)
- ② Adequate fistula diameter (5~6mm or larger)
- ③ Adequate depth that can be punctured with dialysis needle (5~6mm underneath skin)
Autologous graft vs Artificial graft
|
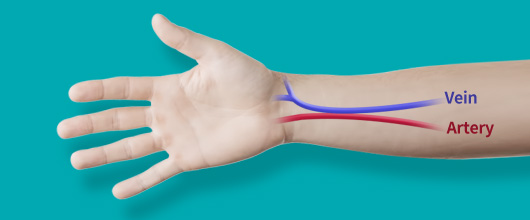
Autologous graft surgery (AVF)
|
Treatment
|
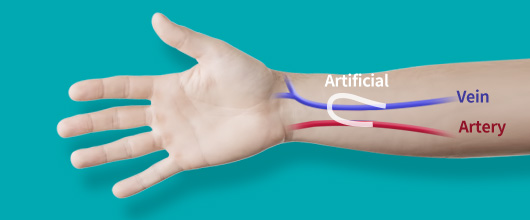
Artificial graft surgery (AVG)
|
| ★★★ |
Difficulty |
★ |
| 2~3 months |
Maturation period |
3~6 weeks |
| Low risk of aneurysm, thrombosis, and infection |
Complication |
High risk of aneurysm, thrombosis, and infection |
| About 2.8~3 years |
Expected average span |
About 2~2.5 years |
surgery
AV fistula corrective surgery
Surgery that treats complication of AV fistula
01
AV fistula reduction
Surgery to treat aneurysm of AV fistula
Good AV fistula must flow in straight line with adequate thickness at adequate depth.
However, if the problems like
- ① excessive blood flow
- ② stenosis at the arterial access (the arterial part where the blood is drawn out with dialysis machine) persists, the fistula swells and dilates extensively.
This is called ‘aneurysm’
Once ‘aneurysm' that enlarges AV fistula and convolute its path, blood flow into the fistula becomes too excessive,
which causes
- ① excessive blood flow
- ② stenosis at the arterial access (the arterial part where the blood is drawn out with dialysis machine) persists, the fistula swells and dilates extensively.
This is called ‘aneurysm’
If such complication arises, it also affects dialysis, so reduction is performed to modify the fistula into more adequate size and straight passage.
-
 AV fistula
Used longer and
AV fistula
Used longer and
healthier
-
 Cardiac failure
Cardiac failure
prevention
Minimal cardiac
stress
-
 Without hemodialytic
Without hemodialytic
catheter
Sustaining
original AV fistula
Treatment result
-
Before the treatment
AV fistula is excessively dilated from the AV anastomosis, creating blood flow so excessive that it stresses the heart.
-
3 months after the treatment
After reduction, the pressure in AV fistula decreases and the blood flow returns to normal
Surgery process
-
Vascular condition
check
- AV fistula ultrasound
- Angiograph
-
Surgery plan and
preparation
- Pre-operation test and preparation
-
Operation
- Local anesthesia and sedation anesthesia
- Problematic fistula resection and suture
-
Recovery
- disinfection in surgical site for next 2~3 weeks
- Hemodialysis possible with the treated site after 3~4 weeks.
After reduction, the pressure in AV fistula decreases and the blood flow returns to normal, decreasing the stress to heart.
In long-term, stenosis in central vein decreases and AV fistula is kept for long period.
02
Pseudoaneurysm resection
Surgery to treat ‘pseudoaneurysm’, the complication of AV fistula.
AV fistula goes through hemostasis process where the puncture by needle persists, then the surrounding tissue slowly blocks the puncture.
The bleeding may not stop if the puncture is made repeatedly on one or two areas and the vascular wall becomes thinner or if complication arises during the recovery process after the surgery.
The blood that leaks from the area where bleeding is not completely sealed off may collect in subcutaneous fat layer, form a sac, and bulge. It is called ‘psuedoaneurysm’.
Pseudoaneurysm is common in AV fistula and it also often can occur autologous AV fistula located deep inside the flesh.
If pseudoaneurysm gets larger, it may cause various complications like sepsis, skin defect (artificial graft fistula), thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, skin infection, vascular rupture (autologous fistula)
Commonly, surgery is performed when there is a problem in vascular wall along with psuedoaneurysm 1cm or larger or when there is thrombus.
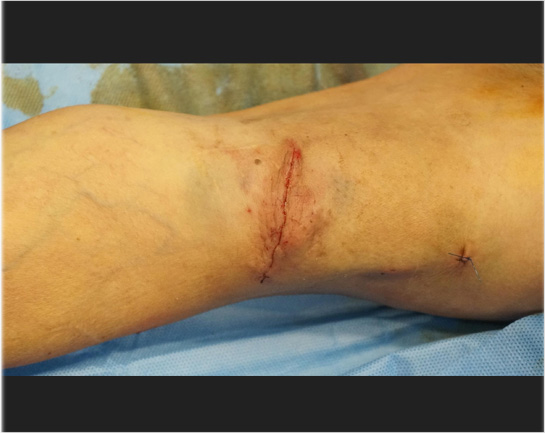
Treatment result
-
Before the treatment
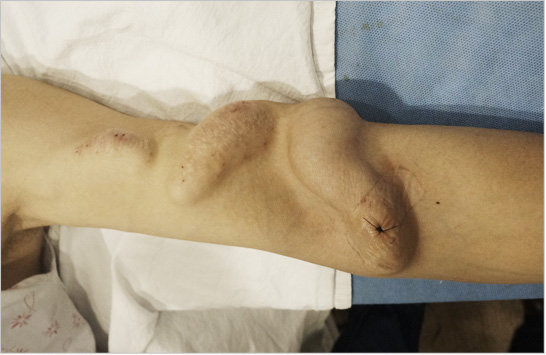
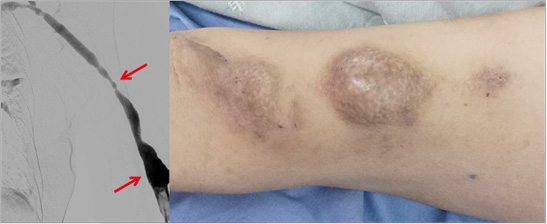
Progressive dilatation of pseudoaneurysm in artificial graft fistula, swelling like a sphere.
-
After the surgery
Correction performed to resect pseudoaneurysm and change the deficit area with artificial vascular graft
03
Vein superficialization
Surgery that relocates deep vein close to the skin
Well-made AV fistula must satisfy ‘3 conditions’ of blood flow, size, and depth.
Particularly, ideal depth is 5~6 mm underneath the skin.
If the fistula is located too deep, the needle can’t puncture the fistula easily and consequently puncture one or two site that is easy to puncture, which increases the risk of pseudoaneurysm.
The reason the veins are located deep is because the veins are hidden inside thick fat layer.
Therefore, vein superficialization is commonly performed with ‘venous lifting (Lifting surgery)’ and ‘Fat layer removal’.
In MINT hospital, we perform hemodialysis access surgery and vein superficialization at the same time for patient’s convenience.
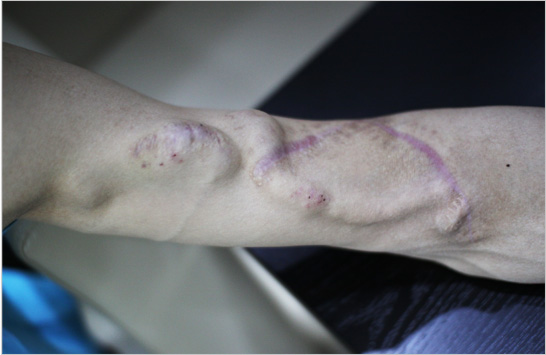
Treatment result
-
Before the treatment
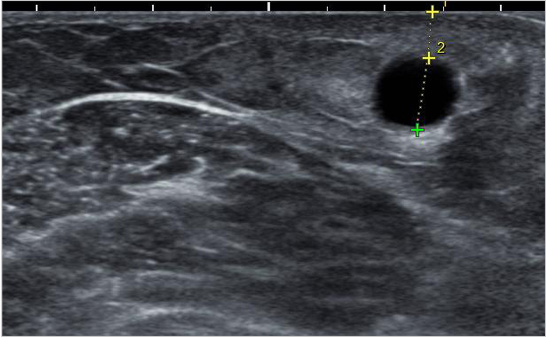
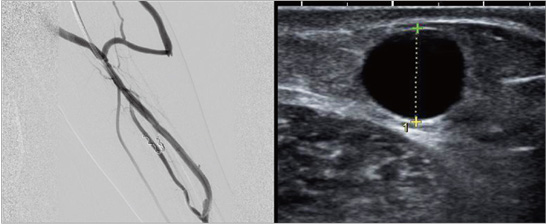
AV fistula is located at 8mm from the surface, which is comparatively deep, making it difficult to puncture with fistula needle.
-
After the surgery
After conducting vein superficialization that lifts AV fistula up, the fistula became closer to the surface, at 4mm.
04
AV fistula streamline surgery
Surgery that streamlines AV fistula into a straight line
when the fistula is too convoluted and is difficult to puncture.
05
Peripheral vascular ligation
When AV fistula does not develop well as the blood flow is stolen by peripheral blood vessels,
the vessels are ligated to stop blood flow.
Hybrid AV fistula treatment
Collaborative treatment of procedure (non-surgical) and surgery
Hybrid treatment is a treatment that is performed at the same time when the treatment area is more than one and non-surgical approach and surgical approach are necessary depending on the site.
For comprehensive treatment, multidisciplinary collaboration is required, It maximizes advantages of non-surgical intravascular treatment and surgical treatment.
-
Recanalization
- From the inside of fistula
- - Recanalization of occluded fistula
- - Expansion of narrowed fistula
- Performed by intervention specialist
- Immediate result, less complication, fast recovery.
-
Surgery
- From the outside of fistula
- - Connection of blood vessels
- - Artificial graft implant
- - Reduction of dilated fistula
- - AV fistula streamlining and superficialization of vein
- Performed by vascular surgeon
- Long-lasting result
(Less unnecessary re-treatment)
+
-
Hybrid treatment
- Management of complex AV fistula problem from inside and outside of the fistula
- multidisciplinary collaboration
- Maximization of advantages of both treatments.
=
-
 Recanalization and
Recanalization and
surgery all at once
Faster and
more reasonable!
-
 All the problems treated
All the problems treated
at once
Greater
efficiency!
-
 Inside and outside
Inside and outside
of AV fistula at the same time
Better
results!
Treatment result
-
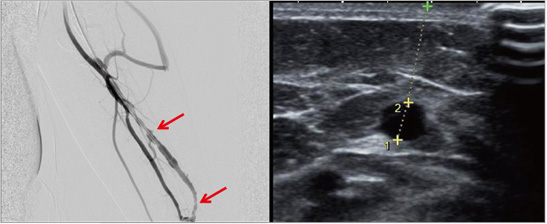
Before the treatment.1
Patient with underdeveloped, deep AV fistula who can’t have dialysis.
-
Treatment summary.1
- ① Narrowed section in the fistula was widened with recanalization from the inside and
- ② Deeply-located vein was relocated near the surface (vein superficialization) For easier dialysis.
-
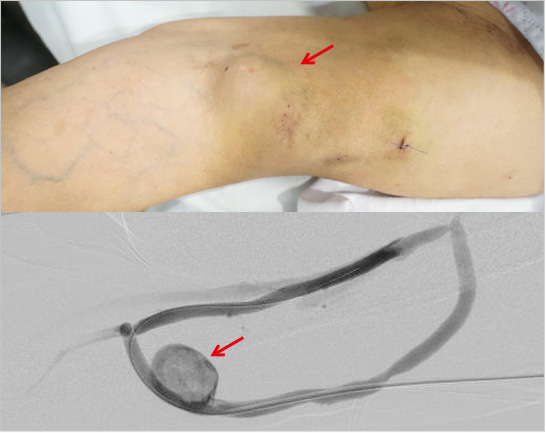
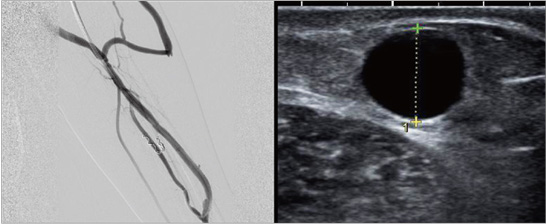
Before the treatment.2
Patient that shows aneurysm with bulging fistula, endovascular wall occluded with thrombus, and stenosis in two sites at the upper part of aneurysm.
-
Treatment summary.2
- ① The stenosis in the upper part of aneurysm was widened with recanalization,
- ② Endovascular thrombus was removed at the same time,
- ③ AV fistula reduction was conducted.
 KakaoTalk
KakaoTalk Blog
Blog Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram YouTube
YouTube NaverTV
NaverTV Korean
Korean Chinese
Chinese Russian
Russian


 Reservation
Reservation
 Home
Home