-
Chronic renal disease
(Chronic renal failure)Damaged or dysfunctional kidney
(persisting over 3 months) -
End-stage renal failure
The condition deteriorates, making the kidney dysfunctional
-
Renal replacement
(Dialysis)- ① Hemodialysis
- ② Peritoneal dialysis
- ③ Renal dialysis
If kidney (Excretion organ that excretes filtered wastes in the blood) is damaged or dysfunctional due to diabetes (50%),
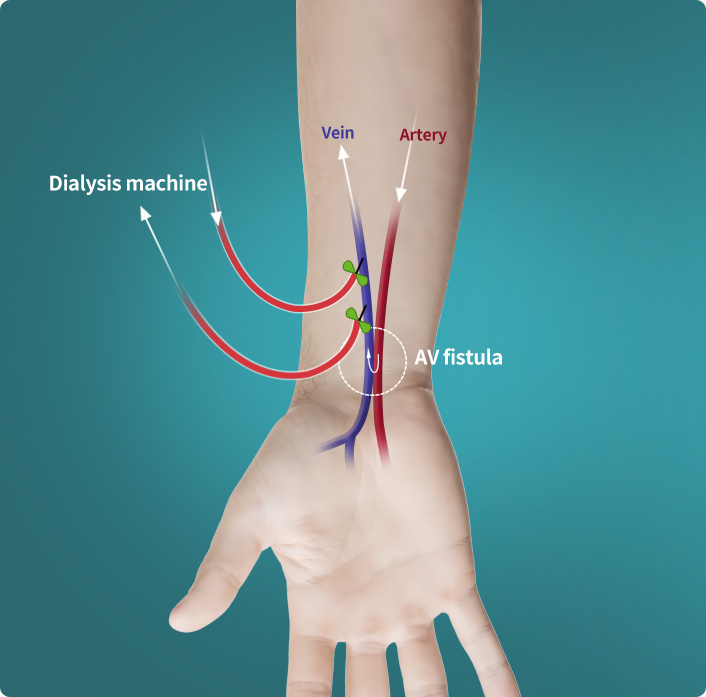
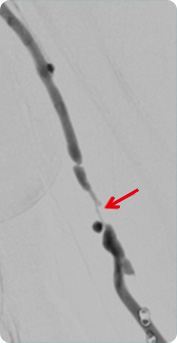
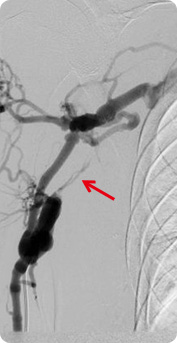
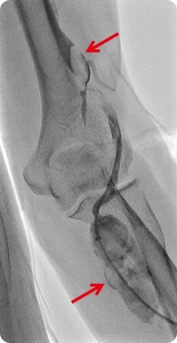
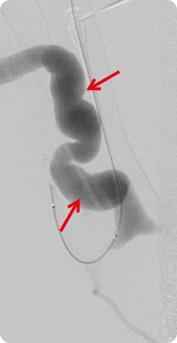
polycystic renal disease, glomerulonephritis, old age, obesity, and hyperlipidemia for over 3 months, it is diagnosed as chronic renal disease (chronic renal failure) If the condition deteriorates and kidney becomes completely dysfunctional, it is called end-stage renal failure, and the most common practice for this occasion is hemodialysis.
Some of the blood is drawn out to dialysis machine to be filtered of waste and then put back into the body. It is conducted about 3 times (4 hours for each session) weekly.
 KakaoTalk
KakaoTalk Blog
Blog Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram YouTube
YouTube NaverTV
NaverTV Korean
Korean Chinese
Chinese Russian
Russian


 Reservation
Reservation
 Home
Home